802.11 Radios consume a lot of power. Hence, a lot of time and effort has been expended in the area of 802.11 Power Save to make the 802.11 Devices more energy efficient. Spatial Multiplexing Power save is one such methodology which allows the 802.11 device to save more power.
The 802.11 Standard in 802.11n and later standards allowed the use of MIMO rates and use of multiple spatial streams. The use of multiple spatial streams requires the use of multiple antennas. By enabling multiple antennas more battery power is used.
To optimize the use of using multiple antennas -Spatial Multiplexing power save mechanism was introduced.
Spatial Multiplexing Power-Save tries to reduce power consumption by either dynamically switching on/off the number of antennas to a single TX/RX Antenna set or statically configuring the 802.11 device to a single TX/RX antenna.
The two methodologies of SMPS are
- Dynamic SMPS – Dynamically enable multiple antennas on the indication of an impending data traffic RX
- Static SMPS – notify the Access Point that the 802.11 Station would be configured to lower antenna configuration indicating that the 802.11 Station does not require a higher antenna configuration.
SM Power-Save Negotiation
Spatial Multiplexing Power Save capability support is advertised in the HT Capability Information Element in the beacon/Probe Response/Association Response by the Access Point and in the Probe Request/association request frame sent by the Station. The SMPS field and its interpretation are provided below
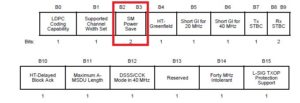

Fig Courtesy: 802.11 Standard