The Raw socket can be used to send and receive data from the L2 layer directly. To achieve this, a suitable socket protocol type needs to be sent out. we will use ETH_P_ARP for the ARP L2 protocol. The sample code only transmits a single ARP packet. An interested reader can add the receive code and modify it to suit their needs.
The intent of this article is not to provide an implementation of ARP (though it gives a nice start point). ARP as a protocol can be learnt via its various online resources. Wikipedia would be a good place to start.
The example code provides only a means of sending a L2 layer packet directly from the application. ARP as the protocol for this code was chosen as it is easy to create the header for the same. An interested reader can prefer to choose other L2 layer headers and try the code out.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <linux/if_ether.h>
#include <linux/if_packet.h>
#include <bits/ioctls.h>
#include <linux/if_arp.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define DEBUG 1
struct sockaddr_ll *L2_sock_addr = NULL, *L2_sock_dest = NULL;
struct ifreq ifr = {0};
int raw_socket;
extern int errno;
/* Interrupt_handler – so that CTRL + C can be used to
* exit the program */
void interrupt_handler (int signum) {
close(raw_socket);
free(L2_sock_addr);
exit(0);
}
#if DEBUG
/* print the packet */
void dumpmsg(unsigned char *recvbuffer, int length) {
int count_per_length = length, i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < count_per_length; i++) {
printf(“%02x “, recvbuffer[i]);
}
printf(“\n”);
}
#endif
/* from header if_arp.h for ethernet */
struct ARP_source_dest {
unsigned char ar_sha[ETH_ALEN]; /* sender hardware address */
unsigned char ar_sip[4]; /* sender IP address */
unsigned char ar_tha[ETH_ALEN]; /* target hardware address */
unsigned char ar_tip[4]; /* target IP address */
};
void main () {
socklen_t length, num_of_bytes;
unsigned short hardware_type = 0x1;
unsigned char buffer[128] = {0};
unsigned char recvbuffer[1024] = {0};
char *interface_name = “enp0s3”; /*interface name on my system*/
struct arphdr *ARP_hdr;
struct ethhdr *eth_hdr;
struct ARP_source_dest *arp_source_dest;
int index,error, ifindex;
signal (SIGINT, interrupt_handler);
signal (SIGTERM, interrupt_handler);
if (0 > (raw_socket = socket(AF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ARP)))) {
printf(“Unable to create a socket\n”);
exit(0);
}
L2_sock_addr = (struct sockaddr_ll *)malloc(sizeof(struct sockaddr_ll));
if (L2_sock_addr == NULL) {
printf(“unable to allocate socket address memory\n”);
goto end;
}
strncpy(ifr.ifr_name, interface_name, strlen(interface_name));
/* get the index number of the current interface */
if (-1 == ioctl(raw_socket, SIOCGIFINDEX, &ifr)) {
printf(“unable to get index of interface\n”);
goto end1;
}
ifindex = ifr.ifr_ifindex;
/* Get the HW MACADDRESS of the interface */
if (-1 == (ioctl(raw_socket, SIOCGIFHWADDR, &ifr))) {
printf(“unable to obtain HW MAC address\n”);
goto end1;
}
/* Fill the socket destination to send to */
L2_sock_addr->sll_family = AF_PACKET;
L2_sock_addr->sll_ifindex = ifindex;
L2_sock_addr->sll_protocol = htons(ETH_P_ARP);
L2_sock_addr->sll_hatype = htons(ARPHRD_ETHER);
L2_sock_addr->sll_pkttype = (PACKET_BROADCAST);
L2_sock_addr->sll_halen = ETH_ALEN;
L2_sock_addr->sll_addr[6] = 0x00;
L2_sock_addr->sll_addr[7] = 0x00;
eth_hdr = (struct ethhdr *)buffer;
for (index = 0; index < ETH_ALEN; index++) {
eth_hdr->h_source[index] = ifr.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data[index];
L2_sock_addr->sll_addr[index] = ifr.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data[index];
}
printf(“macaddress of current device is %02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x\n”, eth_hdr->h_source[0], eth_hdr->h_source[1],
eth_hdr->h_source[2], eth_hdr->h_source[3],
eth_hdr->h_source[4], eth_hdr->h_source[5]);
/* Fill in the ethernet header and ARP headers */
eth_hdr->h_dest[0] = 0xff;
eth_hdr->h_dest[1] = 0xff;
eth_hdr->h_dest[2] = 0xff;
eth_hdr->h_dest[3] = 0xff;
eth_hdr->h_dest[4] = 0xff;
eth_hdr->h_dest[5] = 0xff;
eth_hdr->h_proto = htons(ETH_P_ARP);
ARP_hdr = (struct arphdr *) (buffer + sizeof(struct ethhdr));
ARP_hdr->ar_hrd = htons(hardware_type); /* ethernet */
ARP_hdr->ar_pro = htons(ETH_P_IP); /* IP */
ARP_hdr->ar_hln = ETH_ALEN; /* length of MAC Address */
ARP_hdr->ar_pln = 4; /* length of ipv4 address */
ARP_hdr->ar_op = htons(ARPOP_REQUEST); /* ARP Request */
arp_source_dest = (struct ARP_source_dest *) (buffer + sizeof(struct ethhdr) + sizeof(struct arphdr));
arp_source_dest->ar_sha[0] = eth_hdr->h_source[0]; /* sender HW address */
arp_source_dest->ar_sha[1] = eth_hdr->h_source[1];
arp_source_dest->ar_sha[2] = eth_hdr->h_source[2];
arp_source_dest->ar_sha[3] = eth_hdr->h_source[3];
arp_source_dest->ar_sha[4] = eth_hdr->h_source[4];
arp_source_dest->ar_sha[5] = eth_hdr->h_source[5];
arp_source_dest->ar_sip[0] = 192; /* IP address of sender */
arp_source_dest->ar_sip[1] = 168;
arp_source_dest->ar_sip[2] = 1;
arp_source_dest->ar_sip[3] = 2;
arp_source_dest->ar_tip[0] = 192; /*Destination IP address */
arp_source_dest->ar_tip[1] = 168;
arp_source_dest->ar_tip[2] = 1;
arp_source_dest->ar_tip[3] = 10;
#if DEBUG
dumpmsg((unsigned char *)buffer, (sizeof(struct ethhdr) + sizeof(struct arphdr)+ sizeof(struct ARP_source_dest)));
#endif
num_of_bytes = sendto(raw_socket, buffer,(sizeof(struct ethhdr) + sizeof(struct arphdr) + sizeof(struct ARP_source_dest)), 0,
(struct sockaddr *)L2_sock_addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_ll));
if (-1 == num_of_bytes) {
error = errno;
printf(“value of error is :: %s\n”, strerror(error));
}
end1:
free(L2_sock_addr);
end:
close(raw_socket);
}
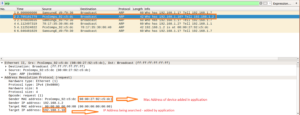
The below Wireshark capture shows the packet that is transmitted
Pingback: Raw Socket Communication with Data Link Layer | Hitch Hiker's Guide to Learning